WhatsApp has continuously evolved to enhance user experience, and one of its most anticipated features, voice note transcription, is finally rolling out. This new option allows users to convert voice messages into text, making communication more convenient when listening to audio isn’t feasible. But how does it work, and what does it mean for WhatsApp users? Let’s tell you!
How Does WhatsApp’s Voice Note Transcription Work?
WhatsApp’s transcription feature automatically converts voice messages into text using on-device processing, ensuring that messages are transcribed directly on your phone without being sent to external servers.
When a user receives a voice message, they must press and hold the message to bring up the options, including the “Transcribe” feature. This feature supports multiple languages. Additionally, transcriptions can be saved and searched later, making it easier to reference important messages without having to replay the audio.
How to Enable Voice Note Transcription
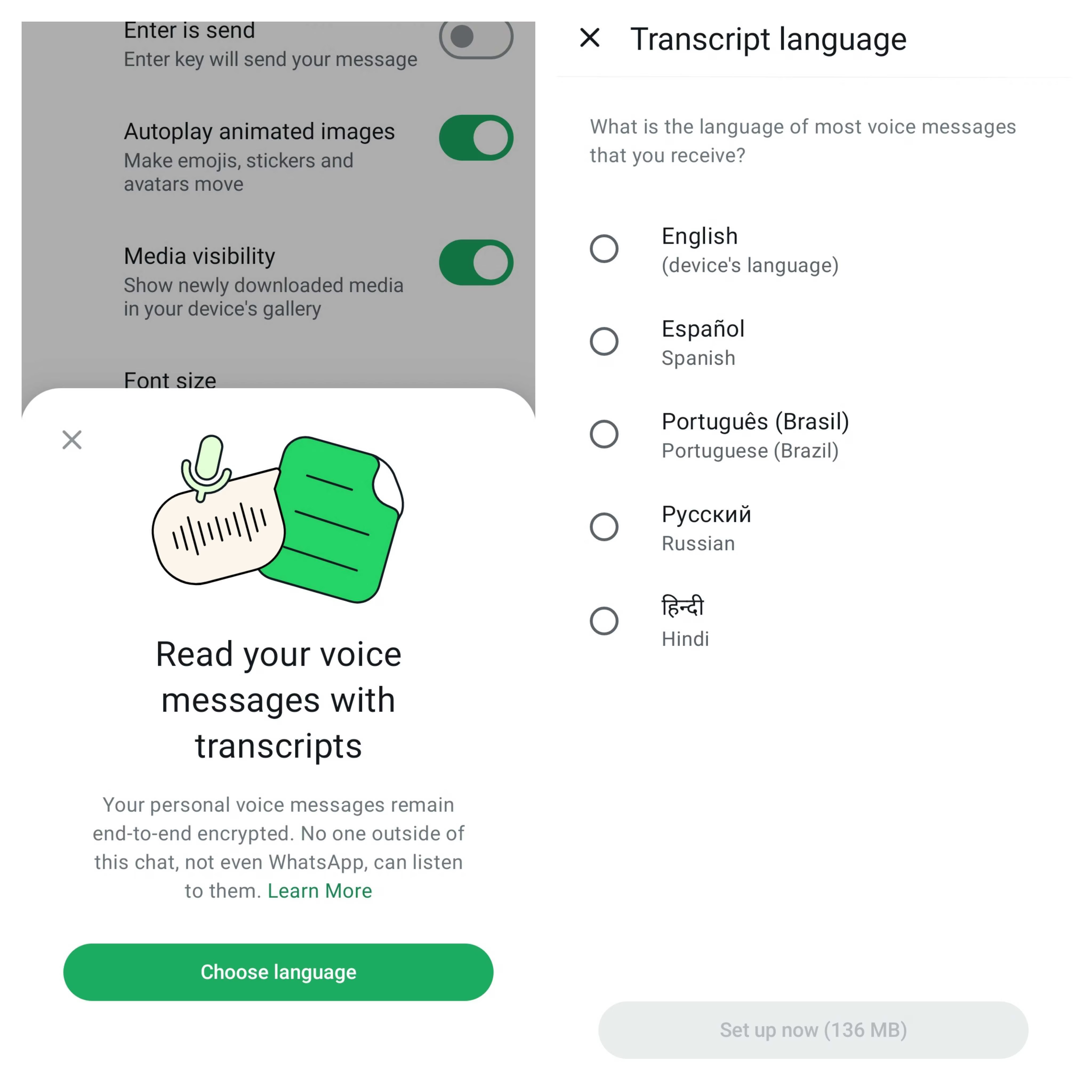
The feature can be activated through WhatsApp’s Settings > Chats under the “Voice Message Transcription” toggle. Users might also need to download specific language packs to ensure accurate transcriptions.
Why This Feature Matters
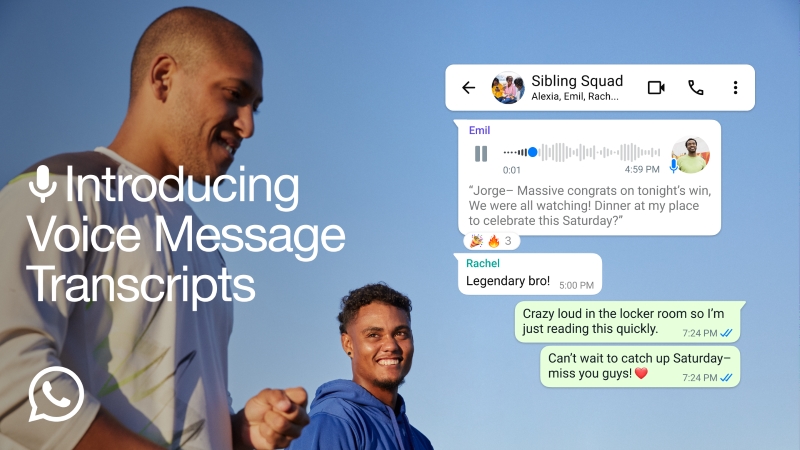
WhatsApp’s transcription enhances accessibility, particularly for users with hearing impairments, by allowing them to read voice messages instead of listening to them. It also improves information retrieval, as users can quickly scan through transcriptions rather than replaying entire voice messages to find key details. Furthermore, since transcriptions occur on-device, the feature aligns with WhatsApp’s commitment to end-to-end encryption, ensuring that messages remain private and secure.
Limitations and Challenges
![]()
Despite its advantages, the transcription feature may face some challenges. Accuracy issues could arise due to background noise, unclear speech, or strong accents, which might affect the quality of transcriptions. Additionally, while WhatsApp is expected to support multiple languages, the initial rollout may be limited to a few primary ones, restricting accessibility for some users.
Another potential challenge is the impact on storage and processing power, as transcriptions occur on-device, meaning older phones with limited storage or lower processing capabilities might struggle with efficiency.







